nzmax is an integer that contains the length of ir, pr, and if it exists, pi. It is the maximum number possible number of nonzero elements in the sparse matrix.
ir points to an integer array of length nzmax containing the row indices of the corresponding elements in pr and pi.
jc points to an integer array of length N+1 that contains column index information. For j in the range 0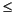
j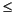
N-1, jc[j] is the index in ir, pr (and pi if it exists) of the first nonzero entry in the jth column and jc[j+1]-1 index of the last nonzero entry. As a result, jc[N] is also equal to nnz, the number of nonzero entries in the matrix. If nnz is less than nzmax, then more nonzero entries can be inserted in the array without allocating additional storage.