pi i 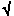 -1
-1j ieps realmin realmax 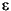 )21023
)21023inf nan | Getting Started with MATLAB | Help Desk |
Expressions
Like most other programming languages, MATLAB provides mathematical expressions, but unlike most programming languages, these expressions involve entire matrices. The building blocks of expressions arenum_students = 25creates a 1-by-1 matrix named
num_students and stores the value 25 in its single element.
Variable names consist of a letter, followed by any number of letters, digits, or underscores. MATLAB uses only the first 31 characters of a variable name. MATLAB is case sensitive; it distinguishes between uppercase and lowercase letters. A and a are not the same variable. To view the matrix assigned to any variable, simply enter the variable name.
MATLAB uses conventional decimal notation, with an optional decimal point and leading plus or minus sign, for numbers. Scientific notation uses the letter e to specify a power-of-ten scale factor. Imaginary numbers uses either i or j as a suffix. Some examples of legal numbers are
3 -99 0.0001 9.6397238 1.60210e-20 6.02252e23 1i -3.14159j 3e5iAll numbers are stored internally using the long format specified by the IEEE floating-point standard. Floating-point numbers have a finite precision of roughly 16 significant decimal digits and a finite range of roughly 10-308 to 10+308. (The VAX computer uses a different floating-point format, but its precision and range are nearly the same.) Expressions use familiar arithmetic operators and precedence rules.
+ addition
- subtraction
* multiplication
/ division
\ left division
\,
is described in the section on Matrices and Linear Algebra in the Using MATLAB book.
^ power
' complex conjugate transpose
( ) specify evaluation order
MATLAB provides a large number of standard elementary mathematical functions, including abs, sqrt, exp, and sin. Taking the square root or logarithm of a negative number is not an error; the appropriate complex result is produced automatically. MATLAB also provides many more advanced mathematical functions, including Bessel and gamma functions. Most of these functions accept complex arguments. For a list of the elementary mathematical functions, type
help elfunFor a list of more advanced mathematical and matrix functions, type
help specfun help elmatSome of the functions, like
sqrt and sin, are built-in. They are part of the MATLAB core so they are very efficient, but the computational details are not readily accessible. Other functions, like gamma and sinh, are implemented in M-files. You can see the code and even modify it if you want.
Several special functions provide values of useful constants.
Infinity is generated by dividing a nonzero value by zero, or by evaluating well defined mathematical expressions that overflow, i.e., exceed realmax. Not-a-number is generated by trying to evaluate expressions like 0/0 or inf-inf that do not have well defined mathematical values.
eps = 1.e-6and then use that value in subsequent calculations. The original function can be restored with
clear epsYou have already seen several examples of MATLAB expressions. Here are a few more examples, and the resulting values.
rho = (1+sqrt(5))/2
rho =
1.6180
a = abs(3+4i)
a =
5
z = sqrt(besselk(4/3,rho-i))
z =
0.3730+ 0.3214i
huge = exp(log(realmax))
huge =
1.7977e+308
toobig = pi*huge
toobig =
Inf