| MATLAB Functions | Help Desk |
erf, erfc, erfcx, erfinv
Error functions
Y = erf(X) Error function Y = erfc(X) Complementary error function Y = erfcx(X) Scaled complementary error function X = erfinv(Y) Inverse of the error functionThe error function
erf(X) is defined as the integral of the Gaussian distribution function from 0 to x: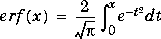 The complementary error function
The complementary error function erfc(X) is defined as: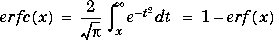 The scaled complementary error function
The scaled complementary error function erfcx(X) is defined as: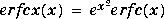 For large
For large X, erfcx(X) is approximately 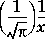 .
.
Y = erf(X)
returns the value of the error function for each element of real array X.
Y = erfc(X)
computes the value of the complementary error function.
Y = erfcx(X)
computes the value of the scaled complementary error function.
X = erfinv(Y)
returns the value of the inverse error function for each element of Y. The elements of Y must fall within the domain 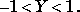
erfinv(1) is Inf
erfinv(-1) is -Inf.
For abs(Y) > 1, erfinv(Y) is NaN.
The relationship between the error function and the standard normal probability distribution is:
x = -5:0.1:5; standard_normal_cdf = (1 + (erf(x*sqrt(2))))./2;For the error functions, the MATLAB code is a translation of a Fortran program by W. J. Cody, Argonne National Laboratory, NETLIB/SPECFUN, March 19, 1990. The main computation evaluates near-minimax rational approximations from [1]. For the inverse of the error function, rational approximations accurate to approximately six significant digits are used to generate an initial approximation, which is then improved to full accuracy by two steps of Newton's method. The M-file is easily modified to eliminate the Newton improvement. The resulting code is about three times faster in execution, but is considerably less accurate. [1] Cody, W. J., "Rational Chebyshev Approximations for the Error Function," Math. Comp., pgs. 631-638, 1969