| MATLAB Functions | Help Desk |
line
Create Line objectline(X,Y)
line(X,Y,Z)
line(X,Y,Z,'PropertyName',PropertyValue,...)
line('PropertyName',PropertyValue,...) Formal-PN/PV pairs only
h = line(...)
line creates a Line object in the current Axes. You can specify the color, width, line style, and marker type, as well as other characteristics.
The line function has two forms:
line(X,Y,Z)MATLAB cycles through the Axes
ColorOrderandLineStyleOrderproperty values the way theplotfunction does. However, unlikeplot,linedoes not call thenewplotfunction.
line with only property name/property value pairs,
line('XData',x,'YData',y,'ZData',z)MATLAB draws a Line object in the current Axes using the default Line color (see the
colordeffunction for information on color defaults). Note that you cannot specify matrix coordinate data with the low-level form of thelinefunction.
line(X,Y)
adds the Line defined in vectors X and Y to the current Axes. If X and Y are matrices of the same size, line draws one Line per column.
line(X,Y,Z)
creates Lines in three-dimensional coordinates.
line(X,Y,Z,'PropertyName',PropertyValue,...)
creates a Line using the values for the property name/property value pairs specified and default values for all other properties.
line('XData',x,'YData',y,'ZData',z,'PropertyName',PropertyValue,...)
creates a Line in the current Axes using the property values defined as arguments. This is the low-level form of the line function, which does not accept matrix coordinate data as the other informal forms described above.
h = line(...)
returns a column vector of handles corresponding to each Line object the function creates.
In its informal form, the line function interprets the first three arguments (two for 2-D) as the X, Y, and Z coordinate data, allowing you to omit the property names. You must specify all other properties as name/value pairs. For example,
line(X,Y,Z,'Color','r','LineWidth',4)The low-level form of the
line function can have arguments that are only property name/property value paris. For example,
line('XData',x,'YData',y,'ZData',z,'Color','r','LineWidth',4)
set and get.
You can specify properties as property name/property value pairs, structure arrays, and cell arrays (see the set and get reference pages for examples of how to specify these data types).
Unlike high-level functions such as plot, line does not respect the setting of the Figure and Axes NextPlot properties. It simply adds Line objects to the current Axes. However, Axes properties that are under automatic control such as the axis limits can change to accommodate the Line within the current Axes.
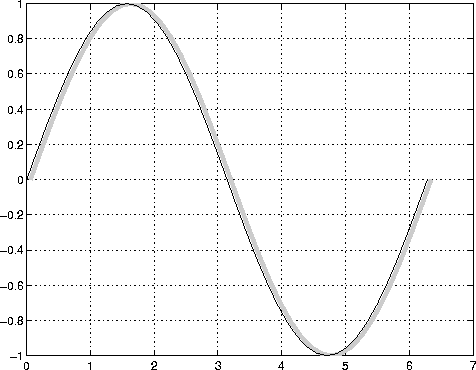
This example uses the line function to add a shadow to plotted data. First, plot some data and save the Line's handle:
t = 0:pi/20:2*pi; hline1 = plot(t,sin(t),'k');Next, add a shadow by offsetting the x coordinates. Make the shadow Line light gray and wider than the default
LineWidth:
hline2 = line(t+.06,sin(t),'LineWidth',4,'Color',[.8 .8 .8]);Finally, pop the first Line to the front:
set(gca,'Children',[hline1 hline2])

Input Argument Dimensions - Informal Form
This statement reuses the one column matrix specified forZData to produce two lines, each having four points.
line(rand(4,2),rand(4,2),rand(4,1))If all the data has the same number of columns and one row each, MATLAB transposes the matrices to produce data for plotting. For example,
line(rand(1,4),rand(1,4),rand(1,4))is changed to:
line(rand(4,1),rand(4,1),rand(4,1))This also applies to the case when just one or two matrices have one row. For example, the statement,
line(rand(2,4),rand(2,4),rand(1,4))is equivalent to:
line(rand(4,2),rand(4,2),rand(4,1))
 You can set default Line properties on the Axes, Figure, and Root levels:
You can set default Line properties on the Axes, Figure, and Root levels:
set(0,'DefaultLinePropertyName',PropertyValue,...)
set(gcf,'DefaultLinePropertyName',PropertyValue,...)
set(gca,'DefaultLinePropertyName',PropertyValue,...)
Where PropertyName is the name of the Line property and PropertyValue is the value you are specifying.
This section lists property names along with the type of values each accepts. Curly braces { } enclose default values.
BusyAction cancel | {queue}
Callback routine interruption. The BusyAction property enables you to control how MATLAB handles events that potentially interrupt executing callback routines. If there is a callback routine executing, subsequently invoked callback routes always attempt to interrupt it. If the Interruptible property of the object whose callback is executing is set to on (the default), then interruption occurs at the next point where the event queue is processed. If the Interruptible property is off, the BusyAction property (of the object owning the executing callback) determines how MATLAB handles the event. The choices are:
cancel - discard the event that attempted to execute a second callback routine.
queue - queue the event that attempted to execute a second callback routine until the current callback finishes.
ButtonDownFcn stringButton press callback routine. A callback routine that executes whenever you press a mouse button while the pointer is over the Line object. Define this routine as a string that is a valid MATLAB expression or the name of an M-file. The expression executes in the MATLAB workspace.
Children vector of handlesThe empty matrix; Line objects have no children.
Clipping {on} | off
Clipping mode. MATLAB clips Lines to the Axes plot box by default. If you set Clipping to off, Lines display outside the Axes plot box. This can occur if you create a Line, set hold to on, freeze axis scaling (axis manual), and then create a longer Line.
Color ColorSpec
Line color. A three-element RGB vector or one of MATLAB's predefined names, specifying the Line color. See the ColorSpec reference page for more information on specifying color.
CreateFcn stringCallback routine executed during object creation. This property defines a callback routine that executes when MATLAB creates a Line object. You must define this property as a default value for Lines. For example, the statement,
set(0,'DefaultLineCreateFcn','set(gca,''LineStyleOrder'',''-.|- -'')')defines a default value on the Root level that sets the Axes
LineStyleOrder whenever you create a Line object. MATLAB executes this routine after setting all Line properties. Setting this property on an existing Line object has no effect.
DeleteFcn string
Delete Line callback routine. A callback routine that executes when you delete the Line object (e.g., when you issue a delete command or clear the Axes or Figure). MATLAB executes the routine before deleting the object's properties so these values are available to the callback routine.
EraseMode {normal} | none | xor | backgroundErase mode. This property controls the technique MATLAB uses to draw and erase Line objects. Alternative erase modes are useful for creating animated sequences, where control of the way individual objects redraw is necessary to improve performance and obtain the desired effect.
normal (the default) -- Redraw the affected region of the display, performing the three-dimensional analysis necessary to ensure that all objects are rendered correctly. This mode produces the most accurate picture, but is the slowest. The other modes are faster, but do not perform a complete redraw and are therefore less accurate.
none - Do not erase the Line when it is moved or destroyed.
xor - Draw and erase the Line by performing an exclusive OR (XOR) with the color of the screen beneath it. This mode does not damage the color of the objects beneath the Line. However, the Line's color depends on the color of whatever is beneath it on the display.
background - Erase the Line by drawing it in the Axes' background color. This damages objects that are behind the erased Line, but Lines are always properly colored.
HandleVisibility {on} | callback | off
Control access to object's handle by command-line users and GUIs. This property determines when an object's handle is visible in its parent's list of children. Handles are always visible when HandleVisibility is on. When HandleVisibility is callback, handles are visible from within callbacks or functions invoked by callbacks, but not from within functions invoked from the command line - a useful way to protect GUIs from command-line users, while permitting their callbacks complete access to their own handles. Setting HandleVisibility to off makes handles invisible at all times - which is occasionally necessary when a callback needs to invoke a function that might potentially damage the UI, and so wants to temporarily hide its own handles during the execution of that function.
callback or off, the object's handle does not appear in its parent's Children property, Figures do not appear in the Root's CurrentFigure property, objects do not appear in the Root's CallbackObject property or in the Figure's CurrentObject property, and Axes do not appear in their parent's CurrentAxes property.
The Root ShowHiddenHandles property can be set to on to temporarily make all handles visible, regardless of their HandleVisibility settings (this does not affect the values of the HandleVisibility properties).
Handles that are hidden are still valid. If you know an object's handle, you can set and get its properties, and pass it to any function that operates on handles. This property is useful for preventing command-line users from accidently drawing into or deleting a Figure that contains only user interface devices (such as a dialog box).
Interruptible {on} | off
Callback routine interruption mode. The Interruptible property controls whether a Line callback routine can be interrupted by subsequently invoked callback routines. Only callback routines defined for the ButtonDownFcn are affected by the Interruptible property. MATLAB checks for events that can interrupt a callback routine only when it encounters a drawnow, figure, getframe, or pause command in the routine.
LineStyle {-} | - - | : | -. | none
Linestyle. This property specifies the line style. The available line styles are:
|
|---|
LineStyle none when you want to place a marker at each point, but do not want the points connected with a Line (see the Marker property).
LineWidth scalar
The width of the Line object. Specify this value in points (1 point = 1/72 inch). The default LineWidth is 0.5 points.
Marker character (see table)
Marker symbol. The Marker property specifies marks that display at data points. You can set values for the Marker property independently from the LineStyle property. Supported markers include:
|
|---|
MarkerEdgeColor ColorSpec | none | {auto}
Marker edge color. The color of the marker or the edge color for filled markers (circle, square, diamond, pentagram, hexagram, and the four triangles). ColorSpec defines the color to use. none specifies no color, which makes nonfilled markers invisible. auto sets MarkerEdgeColor to the same color as the Line's Color property.
MarkerFaceColor ColorSpec | {none} | auto
Marker face color. The fill color for markers that are closed shapes (circle, square, diamond, pentagram, hexagram, and the four triangles). ColorSpec defines the color to use. none makes the interior of the marker transparent, allowing the background to show through. auto sets the fill color to the Axes color, or the Figure color, if the Axes Color property is set to none (which is the default for Axes).
MarkerSize size in points
Marker size. A scalar specifying the size of the marker, in points. The default value for MarkerSize is six points (1 point = 1/72 inch). Note that MATLAB draws the point marker at one-third the specified size.
Parent handleLine's parent. The handle of the Line object's parent Axes. You can move a Line object to another Axes by changing this property to the new Axes handle.
Selected on | off
Is object selected. When this property is on. MATLAB displays selection handles if the SelectionHighlight property is also on. You can, for example, define the ButtonDownFcn to set this property, allowing users to select the object with the mouse.
SelectionHighlight {on} | off
Objects highlight when selected. When the Selected property is on, MATLAB indicates the selected state by drawing handles at each vertex. When SelectionHighlight is off, MATLAB does not draw the handles.
Tag string
User-specified object label. The Tag property provides a means to identify graphics objects with a user-specified label. This is particularly useful when constructing interactive graphics programs that would otherwise need to define object handles as global variables or pass them as arguments between callback routines. You can define Tag as any string.
Type string (read only)
Class of graphics object. For Line objects, Type is always the string 'line'.
UserData matrix
User-specified data. Any data you want to associate with the Line object. MATLAB does not use this data, but you can access it using the set and get commands.
Visible {on} | off
Line visibility. By default, all Lines are visible. When set to off, the Line is not visible, but still exists and you can get and set its properties.
XData vector of coordinates
X-coordinates. A vector of x-coordinates defining the Line. YData and ZData must have the same number of rows. (See "Examples").
YData vector or matrix of coordinates
Y-coordinates. A vector of y-coordinates defining the Line. XData and ZData must have the same number of rows. (See "Examples").
ZData vector of coordinates
Z-coordinates. A vector of z-coordinates defining the Line. XData and YData must have the same number of rows. (See "Examples").
axes,newplot, plot, plot3