| MATLAB Functions | Help Desk |
poly
Polynomial with specified roots
p = poly(A) p = poly(r)
p = poly(A)
where A is an n-by-n matrix returns an n+1 element row vector whose elements are the coefficients of the characteristic polynomial, det(sI - A). The coefficients are ordered in descending powers: if a vector c has n+1 components, the polynomial it represents is 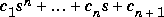 .
.
p = poly(r)
where r is a vector returns a row vector whose elements are the coefficients of the polynomial whose roots are the elements of r.
Note the relationship of this command to
r = roots(p)
p. For vectors, roots and poly are inverse functions of each other, up to ordering, scaling, and roundoff error.
MATLAB displays polynomials as row vectors containing the coefficients ordered by descending powers. The characteristic equation of the matrix
A =
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 0
is returned in a row vector by poly:
p = poly(A)
p =
1 -6 -72 -27
The roots of this polynomial (eigenvalues of matrix A) are returned in a column vector by roots:
r = roots(p)
r =
12.1229
-5.7345
-0.3884
The algorithms employed for poly and roots illustrate an interesting aspect of the modern approach to eigenvalue computation. poly(A) generates the characteristic polynomial of A, and roots(poly(A)) finds the roots of that polynomial, which are the eigenvalues of A. But both poly and roots use EISPACK eigenvalue subroutines, which are based on similarity transformations. The classical approach, which characterizes eigenvalues as roots of the characteristic polynomial, is actually reversed.
If A is an n-by-n matrix, poly(A) produces the coefficients c(1) through c(n+1), with c(1) = 1, in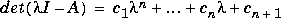 The algorithm is expressed in an M-file:
The algorithm is expressed in an M-file:
z = eig(A);
c = zeros(n+1,1); c(1) = 1;
for j = 1:n
c(2:j+1) = c(2:j+1)-z(j)*c(1:j);
end
This recursion is easily derived by expanding the product.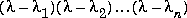 It is possible to prove that
It is possible to prove that poly(A) produces the coefficients in the characteristic polynomial of a matrix within roundoff error of A. This is true even if the eigenvalues of A are badly conditioned. The traditional algorithms for obtaining the characteristic polynomial, which do not use the eigenvalues, do not have such satisfactory numerical properties.
conv Convolution and polynomial multiplication
polyval Polynomial evaluation
residue Convert between partial fraction expansion and polynomial coefficients
roots Polynomial roots