Accenture
Thu, 10/24/2024 - 12:05 — admin
| Publication Type | Thesis |
| Year of Publication | 2024 |
| Authors | Daniel Ramón Lumbierres |
| Academic Department | Dept. Statistics and Operations Research |
| Number of Pages | 124 |
| University | Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya |
| City | Barcelona |
| Degree | PhD Thesis |
| Key Words | supply chain; postponement; stochastic programming; research |
| Abstract | Speculation i Postponement son estratègies oposades de cadena de subministrament dirigides a avançar o postposar els processos de producción que transformen matèries primeres en productes acabats. Un Punt de Desacoblament d’Ordres de Consumidor, o CODP, és un punt logístic de la cadena on la producció especulativa és emmagatzemada fins a l’arribada d’ordres de demanda, de manera que el posicionament de CODPs caracteritza l’estratègia associada a la cadena de subministrament. Es presenten dos models d’optimització per decidir el Disseny en Xarxa de Cadena de Subministrament òptim i la seva estrategia Speculation – Postponement associada mitjançant un enfoc d’optimització estocástica en dues etapes: el primer model, anomenat ( |
| URL | Click Here |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |
Tue, 07/21/2020 - 16:46 — admin
Tue, 07/21/2020 - 15:49 — admin
| Publication Type | Journal Article |
| Year of Publication | 2021 |
| Authors | Daniel Ramón-Lumbierres; F.-Javier Heredia; Joaquim Minguella-Canela; Asier Muguruza-Blanco |
| Journal Title | International Journal of Production Research |
| Pages | 5198-5215 |
| Journal Date | 07/2020 |
| Publisher | Taylor&Francis |
| ISSN Number | 0020-7543 |
| Key Words | manufacturing; postponement; stochastic programming; supply chain network design; 3D printing; additive manufacturing; research; paper |
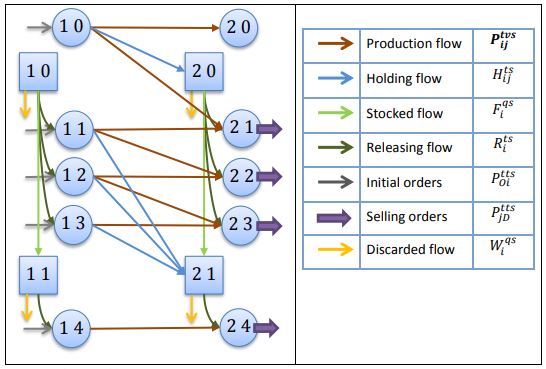
| Abstract | This study presents a new two-stage stochastic programming decision model for assessing how to introduce some new manufacturing technology into any generic supply and distribution chain. It additionally determines the optimal degree of postponement, as represented by the so-called customer order decoupling point (CODP), while assuming uncertainty in demand for multiple products. To this end, we propose here the formulation of a generic supply chain through an oriented graph that represents all the deployable alternative technologies, which are defined through a set of operations that are characterized by lead times and cost parameters. Based on this graph, we develop a mixed integer two-stage stochastic program that finds the optimal manufacturing technology for meeting each market’s demand, each operation’s optimal production quantity, and each selected technology’s optimal CODP. We also present and analyse a case study for introducing additive manufacturing technologies. |
| URL | Click Here |
| DOI | 10.1080/00207543.2020.1775908 |
| Preprint | http://hdl.handle.net/2117/327874 |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |
Wed, 07/11/2018 - 11:30 — admin
| Publication Type | Conference Paper |
| Year of Publication | 2018 |
| Authors | Daniel Ramón-Lumbierres; F.-Javier Heredia; Robert Gimeno Feu; Julio Consola; Román Buil Giné |
| Conference Name | 23th International Symposium on Mathematical Programming |
| Conference Date | 01-06/07/2018 |
| Conference Location | Bordeaux |
| Editor | Mathematical Optimization Society (MOS) |
| Type of Work | contributed presentation |
| Key Words | research; supply chain; postponment; multistage stochastic programming |
| Abstract | Supply chain management has been widely developed through the evolution of manufacturing, distribution, forecasting and customer behavior, encouraging the introduction of postponement strategies in its various forms. At these strategies, semi-finished goods are stored in certain operations of the chain, called decoupling points, waiting for the placement of demand orders, which trigger production flows from decoupling points to the
remainder operations. Such a design problem facing the speculation/postponement paradigm must intrinsically include elements that "unveil" demand orders when they are placed, that is, the modelling approach should keep demand orders as random variables until their placement, when they are disclosed. This work proposes a multi-stage stochastic programming model that decides the optimal allocation of decoupling points, as well as a
process selection among alternative designs for any general supply chain case, where the stochastic parameters, demands by period and product, are represented through a scenario tree, which is in turn generated using the forecasting. Both a risk-neutral model and a risk-aversion approach with stochastic dominance constraints are presented and solved with multi-stage instances of test cases based on real manufacturing problems defined in collaboration with the Accenture consultancy company. |
| URL | Click Here |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |
Fri, 02/16/2018 - 11:58 — admin
 A new website for the research project Strategical Models in Supply Chain Design has been deployed at A new website for the research project Strategical Models in Supply Chain Design has been deployed at
https://gnom.upc.edu/en/projects/supply-chain/smscd-2017
This site is intended to improve the comunication between the different partners of the project (UPC-Accenture Analytics Barcelona - Accenture Labs Silicon Valley) and to show the progress of this project. All the documentacion related with the project is going to be available at this site (meetings, reports, papers, conference contributions), although some of them will be secured. If you would like to acess to some protected document please send an e-mail to f.javier.heredia@upc.edu
Fri, 01/19/2018 - 00:00 — admin
| Publication Type | Tesis de Grau i Màster // BSc and MSc Thesis |
| Year of Publication | 2018 |
| Authors | Sandra Orozco Martín |
| Director | Roman Buil; F.-Javier Heredia; Elena Fernández |
| Tipus de tesi | MSc Thesis |
| Titulació | Interuniversity Master in Statistics and Operations Research UPC-UB |
| Centre | Faculty of Mathematics and Statistics |
| Data defensa | 19/01/2018 |
| Nota // mark | 10 MH (A+) |
| Key Words | teaching; VRP; metaheuristics; MSc Thesis |
| Abstract | In thisThesis, a variant of the Vehicle Routing Problem is considered where products are distributed from a depot to multiple retail stores using capacitated vehicles and not only the transportation cost but also the lost sales resulting from stock-outs at each location are minimized. Given that the real demand of a particular product at some location during a given time period can only be rougthly estimated, a deterministic and dynamic solution is proposed. This solution is divided into two phases: (i) an overnight optimization determines the set of retailers assigned to each vehicle and computes the optimal routes using the available information; (ii) a dynamic model is used separately on each vehicle in order to reoptimize its path according to the new information made available during the execution of the routes. Two exact formulations and two metaheuristics are proposed for the first phase; an exact formulation is implemented for the second phase. Moreover, an end-to-end solution is developed through the implementation of a visualization tool in R Shiny, which uses MySQL databases and shell calls to AMPL to simulate the process of a whole day. |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |
Thu, 08/31/2017 - 23:00 — admin
 A new result of the research project Digitalizing Supply Chain Strategy with 3D Printing with Accenture TechLabs and Center for Analytics has been presented in the Manufacturing Engineering Society International Conference 2017 , MESIC 2017. The study compares different possible production strategies for a product (via conventional technologies and Additive Manufacturing) and assesses the degree of postponement that it would be recommended in order to meet a certain demand distribution. The problem solving is calculated by a program containing a stochastic mathematical model which incorporates extensive information on costs and lead times for the required manufacturing operations. This study was published in Procedia Manufacturing.
Thu, 08/31/2017 - 23:00 — admin
| Publication Type | Proceedings Article |
| Year of Publication | 2017 |
| Authors | J. Minguella-Canela; A. Muguruza; D.R. Lumbierres: F.-Javier Heredia; R. Gimeno; P. Guo; M. Hamilton; K.Shastry, S.Webb |
| Conference Name | Manufacturing Engineering Society International Conference 2017, MESIC 201 |
| Series Title | Procedia Manufacturing |
| Volume | 13 |
| Pagination | 754-761 |
| Conference Start Date | 18/06/2017 |
| Publisher | Elsevier |
| Conference Location | Vigo, Spain |
| Editor | Jorge Salguero, Enrique Ares |
| ISSN Number | 2351-9789 |
| Key Words | Additive Manufacturing; Ultra-postponement; Supply Chain; research; paper |
| Abstract | The best-selling products manufactured nowadays are made in long series along rigid product value chains. Product repetition and continuous/stable manufacturing is seen as a chance for achieving economies of scale. Nevertheless, these speculative strategies fail to meet special customer demands, thus reducing the effective market share of a product in a range. Additive Manufacturing technologies open promising product customization opportunities; however, to achieve it, it is necessary to delay the production operations in order to incorporate the customer’s inputs in the product materialization. The study offered in the present paper compares different possible production strategies for a product (via conventional technologies and Additive Manufacturing) and assesses the degree of postponement that it would be recommended in order to meet a certain demand distribution. The problem solving is calculated by a program containing a stochastic mathematical model which incorporates extensive information on costs and lead times for the required manufacturing operations. |
| URL | Click Here |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1016/j.promfg.2017.09.181 |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |
Thu, 07/27/2017 - 13:34 — admin
| Publication Type | Conference Paper |
| Year of Publication | 2017 |
| Authors | J. Minguella-Canela; A. Muguruza; D.R. Lumbierres; F.-Javier Heredia; R. Gimeno; P. Guo; M. Hamilton; K. Shastry; S. Webb |
| Conference Name | Manufacturing Engineering Society International Conference 2017, MESIC 2017, 28-30 |
| Conference Date | 28-30/07/2017 |
| Publisher | Elsevier |
| Conference Location | Vigo, Spain |
| Type of Work | Contributed presentation |
| Key Words | research; Additive Manufacturing; Ultra-postponement; Supply Chain; stochastic programming |
| Abstract | The best-selling products manufactured nowadays are made in long series along rigid product value chains. Product repetition and continuous/stable manufacturing is seen as a chance for achieving economies of scale. Nevertheless, these speculative strategies fail to meet special customer demands, thus reducing the effective market share of a product in a range. Additive Manufacturing technologies open promising product customization opportunities; however, to achieve it, it is necessary to delay the production operations in order to incorporate the customer’s inputs in the product materialization.
The study offered in the present paper compares different possible production strategies for a product (via conventional technologies and Additive Manufacturing) and assesses the degree of postponement that it would be recommended in order to meet a certain demand distribution. The problem solving is calculated by a program containing a stochastic mathematical model which incorporates extensive information on costs and lead times for the required manufacturing operations. |
| URL | Click Here |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |
Thu, 06/08/2017 - 17:39 — admin
| Publication Type | Funded research projects |
| Year of Publication | 2016 |
| Authors | F.-Javier Heredia |
| Type of participation | Leader |
| Duration | 11/2016-11/2019 |
| Funding organization | Accenture Technology Labs |
| Partners | Accenture Technology Labs (Silicon Valley), Accenture Analytics Innovation Center (Barcelona) |
| Full time researchers | 2 |
| Budget | 132.532,43€ |
| Project code | I-01507, I-01508 |
| Key Words | research; supply chain; manufacturing; private; project; Accenture |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |

|
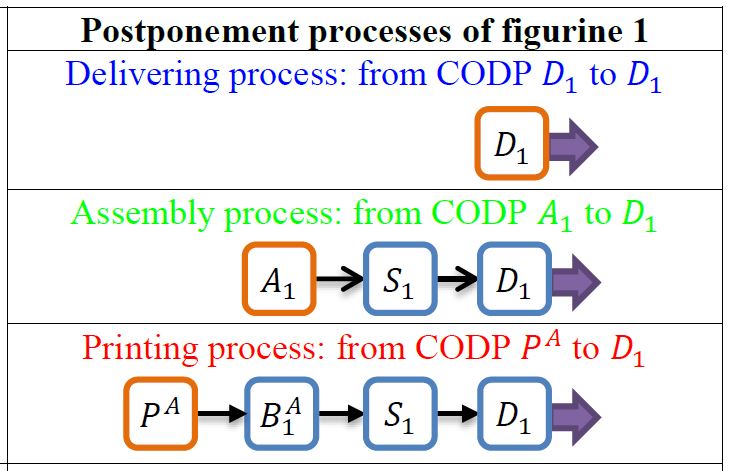 The paper entitled Optimal Postponement in Supply Chain Network Design Under Uncertainty: An Application for Additive Manufacturing (preprint ) has been published in the International Journal of Production Research. This paper is the result of projects Strategical Models in Supply Chain Design, and Digitalizing Supply Chain Strategy with 3D Printing a successful collaboration between GNOM with Accenture Technology Labs (Silicon Valley), Accenture Analytics Innovation Center (Barcelona) and the Fundació CIM-UPC. This study This study presents a new two-stage stochastic programming decision model for assessing how to introduce some new manufacturing technology into any generic supply and distribution chain. It additionally determines the optimal degree of postponement, as represented by the so-called customer order decoupling point (CODP), while assuming uncertainty in demand for multiple products. Finally, it presents and analyses a case study for introducing additive manufacturing technologies.
The paper entitled Optimal Postponement in Supply Chain Network Design Under Uncertainty: An Application for Additive Manufacturing (preprint ) has been published in the International Journal of Production Research. This paper is the result of projects Strategical Models in Supply Chain Design, and Digitalizing Supply Chain Strategy with 3D Printing a successful collaboration between GNOM with Accenture Technology Labs (Silicon Valley), Accenture Analytics Innovation Center (Barcelona) and the Fundació CIM-UPC. This study This study presents a new two-stage stochastic programming decision model for assessing how to introduce some new manufacturing technology into any generic supply and distribution chain. It additionally determines the optimal degree of postponement, as represented by the so-called customer order decoupling point (CODP), while assuming uncertainty in demand for multiple products. Finally, it presents and analyses a case study for introducing additive manufacturing technologies.
 A new website for the research project Strategical Models in Supply Chain Design has been deployed at
A new website for the research project Strategical Models in Supply Chain Design has been deployed at
 A new result of the research project Digitalizing Supply Chain Strategy with 3D Printing with Accenture TechLabs and Center for Analytics has been presented in the Manufacturing Engineering Society International Conference 2017 , MESIC 2017. The study compares different possible production strategies for a product (via conventional technologies and Additive Manufacturing) and assesses the degree of postponement that it would be recommended in order to meet a certain demand distribution. The problem solving is calculated by a program containing a stochastic mathematical model which incorporates extensive information on costs and lead times for the required manufacturing operations. This study was published in Procedia Manufacturing.
A new result of the research project Digitalizing Supply Chain Strategy with 3D Printing with Accenture TechLabs and Center for Analytics has been presented in the Manufacturing Engineering Society International Conference 2017 , MESIC 2017. The study compares different possible production strategies for a product (via conventional technologies and Additive Manufacturing) and assesses the degree of postponement that it would be recommended in order to meet a certain demand distribution. The problem solving is calculated by a program containing a stochastic mathematical model which incorporates extensive information on costs and lead times for the required manufacturing operations. This study was published in Procedia Manufacturing.
