research
A stochastic programming model for the tertiary control of microgrids
Thu, 11/27/2014 - 16:48 — admin| Publication Type | Tesis de Grau i Màster // BSc and MSc Thesis |
| Year of Publication | 2014 |
| Authors | Leire Citores |
| Director | F.-Javier Heredia, Cristina Corchero |
| Tipus de tesi | MSc Thesis |
| Titulació | Master in Statistics and Operations research |
| Centre | Faculty of Mathematics and Statistics |
| Data defensa | 27/06/2014 |
| Nota // mark | 10 MH (A with Honours) |
| Key Words | research; teaching; microgrids, stochastic programming; scenario generation; wind generation; day-ahead electricity market; imbalances; MSc Thesis |
| Abstract | In this thesis a scenario-based two-stage stochastic programming model is proposed to solve a microgrid's tertiary control optimization problem taking into account some renewable energy resource s uncertainty as well uncertain energy deviation prices in the electricity market. Scenario generation methods for wind speed realizations are also studied. Results show that the introduction of stochastic programming represents an improvement over a deterministic model. |
| DOI / handle | http://hdl.handle.net/2099.1/23235 |
| URL | Click Here |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |
Energy Management System para una microrred domestica con participación en los servicios auxiliares de red
Thu, 11/27/2014 - 16:32 — admin| Publication Type | Tesis de Grau i Màster // BSc and MSc Thesis |
| Year of Publication | 2014 |
| Authors | Irune Etxarri Urtasun |
| Director | F.-Javier Heredia, Cristina Corchero |
| Tipus de tesi | MSc Thesis |
| Titulació | Master in Statistics and Operations Reseafrch |
| Centre | Faculty of Mathematics and Statistics |
| Data defensa | 27/06/2014 |
| Nota // mark | ** |
| Key Words | teaching; research; microgrids; stochastic programming; electricity market; secondary reserve; MSc Thesis |
| Abstract | En este proyecto se ha propuesto un modelo estocástico de dos etapas para la gestión de energía en una microrred doméstica, introduciendo la participación en el mercado de banda de regulación. El objetivo del modelo es determinar la potencia que se oferta al mercado diario, teniendo en cuenta la participación en el mercado de banda de regulación. Se ha introducido estocasticidad en los precios de este mercado y en los precios y probabilidades del requerimiento a subir y a bajar de la energía de regulación secundaria. Se han comparado los beneficios de la microrred en caso de participar o no en el mercado de banda de regulación, y se ha visto que la participación en dicho mercado produce grandes beneficios para sus usuarios. |
| DOI / handle | http://hdl.handle.net/2099.1/23233 |
| URL | Click Here |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |
A new paper published in IEEE Transactions on Smart Grids
Wed, 07/30/2014 - 18:27 — admin The paper Optimal Energy Management for a Residential Microgrid Including Vehicle-to-Grid System has been published in IEEE Transactions on Smart Grids. This work, done in collaboration with the Energy Economics group of the Catalonian Institute for Energy Research (IREC), proposes an optimization model to manage a residential microgrid including a charging spot with a vehicle-to-grid system and renewable energy sources. A preprint version of the paper can be downloaded from http://hdl.handle.net/2117/20642
The paper Optimal Energy Management for a Residential Microgrid Including Vehicle-to-Grid System has been published in IEEE Transactions on Smart Grids. This work, done in collaboration with the Energy Economics group of the Catalonian Institute for Energy Research (IREC), proposes an optimization model to manage a residential microgrid including a charging spot with a vehicle-to-grid system and renewable energy sources. A preprint version of the paper can be downloaded from http://hdl.handle.net/2117/20642
Optimal Energy Management for a Residential Microgrid Including a Vehicle-to-Grid System
Sun, 07/20/2014 - 18:34 — admin| Publication Type | Journal Article |
| Year of Publication | 2014 |
| Authors | Lucia Igualada; Cristina Corchero; Miguel Cruz; F-.Javier Heredia |
| Journal Title | IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid |
| Volume | 5 |
| Issue | 4 |
| Pages | 2163-2172 |
| Journal Date | 07/2014 |
| Publisher | IEEE |
| ISSN Number | 1949-3053 |
| Key Words | research; paper; smart grids; vehicle- to-grid (V2G); renewable generation; microgrids; smartgrids; modeling |
| Abstract | An optimization model is proposed to manage a residential microgrid including a charging spot with a vehicle-to-grid system and renewable energy sources. In order to achieve a realistic and convenient management, we take into account: (1) the household load split into three different profiles depending on the characteristics of the elements considered; (2) a realistic approach to owner behavior by introducing the novel concept of range anxiety; (3) the vehicle battery management considering the mobility profile of the owner and (4) different domestic renewable energy sources. We consider the microgrid operated in grid-connected mode. The model is executed one-day-ahead and generates a schedule for all components of the microgrid. The results obtained show daily costs in the range of 2.82 to 3.33 ; the proximity of these values to the actual energy costs for Spanish households validate the modeling. The experimental results of applying the designed managing strategies show daily costs savings of nearly 10%. |
| URL | Click Here |
| DOI | 10.1109/TSG.2014.2318836 |
| Preprint | http://hdl.handle.net/2117/20642 |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |
New national-funded research project
Sat, 07/19/2014 - 12:10 — admin
 The research project Forecasting and optimization of wind generation in energy markets (FOWGEM) has been accepted for granting by the Spanish's National Program of R+D+i for the Challenges of the Society. This is a project coordinated by the Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (the project leaders are prof. Ma. Pilar Muñoz and prof. F.-Javier Heredia) in collaboration with the Universidad Pontificia de Comillas (where the leader is leader prof. Andrés Ramos). Besides these two universities, several other universities and electrical utilities from Spain and abroad participate in the project:
The research project Forecasting and optimization of wind generation in energy markets (FOWGEM) has been accepted for granting by the Spanish's National Program of R+D+i for the Challenges of the Society. This is a project coordinated by the Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (the project leaders are prof. Ma. Pilar Muñoz and prof. F.-Javier Heredia) in collaboration with the Universidad Pontificia de Comillas (where the leader is leader prof. Andrés Ramos). Besides these two universities, several other universities and electrical utilities from Spain and abroad participate in the project:
-
Universities: Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (Catalonia, Spain); Euskal Herriko Unibersitatea (Basc Country, Spain); Universidade Paulista Júlia de Mesquita Filho (Brasil); North Carolina State University (USA).
-
Electrical Utilities and research centers: Iberdrola, Gas Natural - Fenosa, Catalonia Institute for Energy Research
Forecasting and optimization of wind generation in energy markets
Sat, 07/19/2014 - 11:53 — admin| Publication Type | Funded research projects |
| Year of Publication | 2014 |
| Authors | F.- Javier Heredia; Ma. Pilar Muñoz; Josep Anton Sánchez; Maria Dolores Márquez; Eugenio Mijangos; Marlyn Dayana Cuadrado Guevara |
| Type of participation | Principal Investigator (IP) |
| Duration | 01/2014-12/2016 |
| Call | PROGRAMA ESTATAL DE INVESTIGACIÓN, DESARROLLO E INNOVACIÓN ORIENTADA A LOS RETOS DE LA SOCIEDAD |
| Funding organization | Ministry of Economy and Competitivity, Government of Spain |
| Partners | Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya; Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (Catalonia) Euskal Herriko Unibersitatea (Basc Country) Universidad Pontificia de Comillas (Madrid) Universidade Paulista Júlia de Mesquita Filho (Brasil) North Carolina State University (USA) Electrical Utilities: Iberdrola, Gas Natural - Fenosa. Research centers: Catalonia Institute for Energy Research. |
| Full time researchers | 4,5 |
| Budget | 49.000€ |
| Project code | MTM2013-48462-C2-1-R |
| Key Words | research; MTM2013-48462; forecasting, optimization, wind generation, energy markets; mineco; competitive; public; project; energy |
| Abstract | The coordinated project " Forecasting and Optimization of Wind Generation in Energy Markets" ( FOWGEM) aims at aplying a global approach to the problem of the optimal integration of the wind-enery generation of a generation company in the wholesale electricity market through the combination of statistical forecasting models, mathematical programming models for electricity markets and optimization algorithms. In the framework of the Spanish Strategy for Science and Technology and Innovation 2013-2020 this project contributes fundamentally to challenge 3, " safe, sustainable and clean energy ." Indeed, the forecasting and optimization models and procedures that will be developed in this project, are the necessary mechanisms to allow the competitive and safe integration of wind-energy generation in the multiple-markets based wholesale national energy production system. The FOWGEM project adopts an original and global approach to this problem that combines advanced methodologies in the area of statistics, mathematical modeling of energy markets and theoretical and computatitonal optimization that were developed in several previous projects of the Plan Nacional by the groups of the Universidad Politècnica de Catalunya and the Universidad Pontificia de Comillas . The main objecives of the project are:
|
| URL | Click Here |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |
New research reports on energy markets and smartgrids.
Fri, 01/24/2014 - 10:18 — admin-
 Simona Sacripante, F.-Javier Heredia, Cristina Corchero, Stochastic optimal sale bid for a wind power producer,Research Report DR 2013/06 Dept. of Statistics and Operations Research. E-Prints UPC, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, 2013.
Simona Sacripante, F.-Javier Heredia, Cristina Corchero, Stochastic optimal sale bid for a wind power producer,Research Report DR 2013/06 Dept. of Statistics and Operations Research. E-Prints UPC, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, 2013.
-
F.-Javier Heredia, Julian Cifuentes, Cristina Corchero, Stochastic optimal generation bid to electricity markets with emission risk constraints, Research Report DR 2013/05 Dept. of Statistics and Operations Research. E-Prints UPC, http://hdl.handle.net/2117/20640. Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, 2013.
-
Lucia Igualada, Cristina Corchero, Miguel Cruz-Zambrano, F.-Javier Heredia, Optimal energy management for a residential microgrid including a vehicle-to-grid system, Research Report DR 2013/04 Dept. of Statistics and Operations Research. E-Prints UPC, http://hdl.handle.net/2117/20642 . Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, 2013.
Optimal energy management for a residential microgrid including a vehicle-to-grid system
Mon, 11/18/2013 - 16:34 — admin| Publication Type | Report |
| Year of Publication | 2013 |
| Authors | Lucía Igualada; Cristina Corchero; Miguel Cruz-Zambrano; F.-Javier Heredia |
| Pages | 9 |
| Date | 11/2013 |
| Reference | Research report DR 2013/05, Dept. of Statistics and Operations Research. E-Prints UPC, http://hdl.handle.net/2117/20642. Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya |
| Prepared for | Published at IEEE Transactions on Smart Grids (DOI: 10.1109/TSG.2014.2318836) |
| Key Words | research; optimal management; smart grids; vehicle-to-grid; renewable generation; microgrids |
| Abstract | An optimization model is proposed to manage a residential microgrid including a charging spot with a vehicle-to-grid system and renewable energy sources. In order to achieve a realistic and convenient management, we take into account: (1) the household load split into three different profiles depending on the characteristics of the elements considered; (2) a realistic approach to owner behavior by introducing the novel concept of range anxiety; (3) the vehicle battery management considering the mobility profile of the owner and (4) different domestic renewable energy sources. We consider the microgrid operated in grid-connected mode. The model is executed one-day-ahead and generates a schedule for all components of the microgrid. The results obtained show daily costs in the range of 2.82€ to 3.33€; the proximity of these values to the actual energy costs for Spanish households validate the modeling. The experimental results of applying the designed managing strategies show daily costs savings of nearly 10%. |
| URL | Click Here |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |
Stochastic optimal generation bid to electricity markets with emission risk constraints.
Sun, 11/17/2013 - 19:22 — admin| Publication Type | Report |
| Year of Publication | 2013 |
| Authors | F.-Javier Heredia; Julian Cifuentes; Cristina Corchero |
| Pages | 21 |
| Date | 09/2013 |
| Reference | Research report DR 2013/04, Dept. of Statistics and Operations Research. E-Prints UPC, http://hdl.handle.net/2117/20640. Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya |
| Prepared for | submitted |
| Key Words | research; OR in Energy; Stochastic Programming; Risk Management; Electricity market; Emission reduction |
| Abstract | There are many factors that influence the day-ahead market bidding strategies of a generation company (GenCo) in the current energy market framework. Environmental policy issues have become more and more important for fossil-fuelled power plants and they have to be considered in their management, giving rise to emission limitations. This work allows investigating the influence of the emission reduction plan, and the incorporation of the derivatives medium-term commitments in the optimal generation bidding strategy to the day-ahead electricity market. Two different technologies have been considered: the coal thermal units, high-emission technology, and the combined cycle gas turbine units, low-emission technology. The Iberian Electricity Market (MIBEL) and the Spanish National Emission Reduction Plan (NERP) defines the environmental framework to deal with by the day-ahead market bidding strategies. To address emission limitations, some of the standard risk management methodologies developed for financial markets, such as Value-at-Risk (VaR) and Conditional Value-at-Risk (CVaR), have been extended giving rise to the new concept of Conditional Emission-at-Risk (CEaR). This study offers to electricity generation utilities a mathematical model to determinate the individual optimal generation bid to the wholesale electricity market, for each one of their generation units that maximizes the long-run profits of the utility abiding by the Iberian Electricity Market rules, as well as the environmental restrictions set by the Spanish National Emissions Reduction Plan. The economic implications for a GenCo of including the environmental restrictions of this National Plan are analyzed, and the effect of the NERP in the expected profits and optimal generation bid are analyzed. |
| URL | Click Here |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |
New paper published in the International Statistical Review.
Fri, 09/06/2013 - 16:19 — admin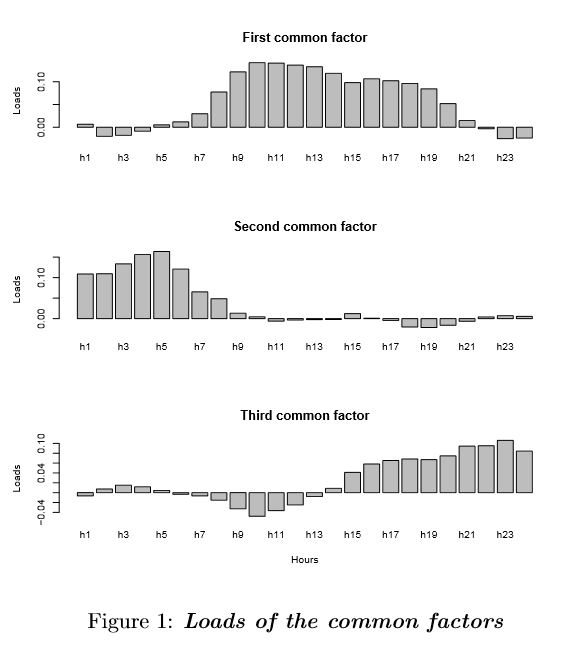 The paper Improving Electricity Market Price Forecasting with Factor Models for the Optimal Generation Bid has been recently published in the journal International Statistical Review (preprint available at http://hdl.handle.net/2117/3047 ). In this article, we apply forecasting factor models to the market framework in Spain and Portugal and study their performance. Although their goodness of fit is similar to that of autoregressive integrated moving average models, they are easier to implement. The second part of the paper uses the spot-price forecasting model to generate inputs for a stochastic programming model, which is then used to determine the company's optimal generation bid. This work is a partial result of the tasks developped in the research project DPI2008-02153 of the MINECO.
The paper Improving Electricity Market Price Forecasting with Factor Models for the Optimal Generation Bid has been recently published in the journal International Statistical Review (preprint available at http://hdl.handle.net/2117/3047 ). In this article, we apply forecasting factor models to the market framework in Spain and Portugal and study their performance. Although their goodness of fit is similar to that of autoregressive integrated moving average models, they are easier to implement. The second part of the paper uses the spot-price forecasting model to generate inputs for a stochastic programming model, which is then used to determine the company's optimal generation bid. This work is a partial result of the tasks developped in the research project DPI2008-02153 of the MINECO.
