The Goal Stack
 PREVIOUS
NEXT
PREVIOUS
NEXT
| ILOG CPLEX 11.0 User's Manual > Advanced Programming Techniques > Using Goals > The Goal Stack |
The Goal Stack |
INDEX
 PREVIOUS
NEXT
PREVIOUS
NEXT
|
To understand how goals are executed, consider the concept of the goal stack. Every node has its own goal stack. When cplex.solve(goal) is called, the goal stack of the root node is simply initialized with goal and then the regular cplex.solve method is called.
When ILOG CPLEX processes a node, it pops the first goal from the node's goal stack and calls method execute. If a nonempty goal is returned, it is simply pushed back on the stack. ILOG CPLEX keeps doing this until the node becomes inactive or the node's goal stack becomes empty. When the node stack is empty, ILOG CPLEX continues with its built-in search strategy for the subtree rooted at this node.
In light of the goal stack, here are the different types of goals:
Or goal creates child nodes. ILOG CPLEX first initializes the goal stack of every child node with a copy of the remaining goal stack of the current node. Then it pushes the goal passed as the argument to the Or goal on the goal stack of the corresponding node. Finally, the current node is deactivated, and ILOG CPLEX continues search by picking a new active node from the tree to process.
And goal simply pushes the goals passed as arguments onto the goal stack in reverse order. Thus, when the goals are popped from the stack for execution, they will be executed in the same order as they were passed as arguments to the And goal.
With this understanding, consider further what really goes on when a goal returns
return AndGoal(OrGoal(var <= IloFloor(val), var >= IloFloor(val)+1), this); |
The And goal is pushed onto the current node's goal stack, only to be immediately popped back off of it. When it is executed, it will push this on the goal stack and then the Or goal. Thus, the Or goal is the next goal that ILOG CPLEX pops and executes. The Or goal creates two subnodes, and initializes their goal stacks with copies of the goal stack of the current node. At this point both subnodes will have this on top of their goal stacks. Next, the Or goal will push a local cut goal for 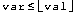 (where
(where 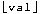 denotes the floor of
denotes the floor of val) on the goal stack of the first subnode. Similarly, it pushes a local cut goal for var 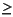
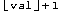 on the goal stack of the second subnode. Finally, the current node is deactivated and ILOG CPLEX continues its search with a new active node from the tree.
on the goal stack of the second subnode. Finally, the current node is deactivated and ILOG CPLEX continues its search with a new active node from the tree.
When ILOG CPLEX processes one of the subnodes that have been created by the Or goal, it will pop and execute the first goal from the node's goal stack. As you just saw, this will be a local cut goal. Thus ILOG CPLEX adds the constraint to the node problem and re-solves the relaxation. Next, this will be popped from the goal stack and executed. This means that the same search strategy as implemented in the original goal is applied at that node.
| Copyright © 1987-2007 ILOG S.A. All rights reserved. Legal terms. | PREVIOUS NEXT |