Convexity
 PREVIOUS
NEXT
PREVIOUS
NEXT
| ILOG CPLEX 11.0 User's Manual > Continuous Optimization > Solving Problems with Quadratic Constraints (QCP) > Identifying a Quadratically Constrained Program (QCP) > Convexity |
Convexity |
INDEX
 PREVIOUS
NEXT
PREVIOUS
NEXT
|
The inequality x2 + y2 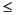 1 is convex. To give you an intuitive idea about convexity, Figure 13.1 graphs that inequality and shades the area that it defines as a constraint. If you consider a and b as arbitrary values in the domain of the constraint, you see that any continuous line segment between them is contained entirely in the domain.
1 is convex. To give you an intuitive idea about convexity, Figure 13.1 graphs that inequality and shades the area that it defines as a constraint. If you consider a and b as arbitrary values in the domain of the constraint, you see that any continuous line segment between them is contained entirely in the domain.
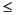 1 is convex
1 is convex
The inequality x2 + y2 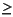 1 is not convex; it is concave. Figure 13.2 graphs that inequality and shades the area that it defines as a constraint. If you consider c and d as arbitrary values in the domain of this constraint, then you see that there may be continuous line segments that join the two values in the domain but pass outside the domain of the constraint to do so.
1 is not convex; it is concave. Figure 13.2 graphs that inequality and shades the area that it defines as a constraint. If you consider c and d as arbitrary values in the domain of this constraint, then you see that there may be continuous line segments that join the two values in the domain but pass outside the domain of the constraint to do so.
 1 is not convex
1 is not convex
It might be less obvious at first glance that the equality x2 + y2 = 1 is not convex either. As you see in Figure 13.3, there may be a continuous line segment that joins two arbitrary points, such as e and f, in the domain but the line segment may pass outside the domain. Another way to see this idea is to note that an equality constraint is algebraically equivalent to the intersection of two inequality constraints of opposite sense, and you have already seen that at least one of those quadratic inequalities will not be convex. Thus, the equality is not convex either.
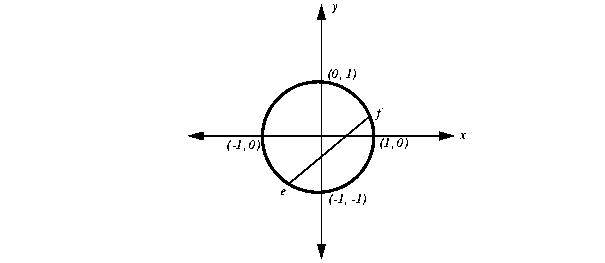
| Copyright © 1987-2007 ILOG S.A. All rights reserved. Legal terms. | PREVIOUS NEXT |