Docència
Mon, 08/19/2019 - 18:04 — admin
| Publication Type | Tesis de Grau i Màster // BSc and MSc Thesis |
| Year of Publication | 2019 |
| Authors | Roger Serra Castilla |
| Director | F.- Javier Heredia; Marlyn D. Cuadrado |
| Tipus de tesi | BSc Thesis |
| Titulació | Grau en Estadística |
| Centre | Facultat de matemàtiques i Estadística |
| Data defensa | 01/2019 |
| Nota // mark | 9.0 |
| Key Words | teaching; scenario generation; scenario trees; electricity markets; BSc Thesis |
| Abstract | The electricity markets (EM) is a regulated system which allows producers and consumers to sell and buy energy at a given price that is fixed through an auction mechanism. Thanks to the tasks done by this system, the safe generation, transportation and distribution of electricity needed to satisfy the demand of the national population is assured. The electricity markets is made up of several markets, that can be considered either spot markets (day-ahead and intraday markets, whose trading commodity is energy) or ancillary services markets (the commodity negotiated is energy used to assure the stability of the energy delivering).
On the other hand, interacting with the EM there is a wind power plant (WPP) which is in charge of the wind power energy production. A battery energy storage system (BESS) is usually associated to the WPP. The union of the WPP and the BESS is called virtual power plant (VPP).
In this context, an optimization model can be presented: the WBVPP model (WPP+BESS Virtual Power Plant). The aim of this optimization model is the maximization of the expected value of the total profit of the VPP. To calculate this value, it is necessary to quantify the amount of wind power energy that fluctuates between the VPP and the EM, as well as the clearing prices of the auctions.
The main purpose of this project is to obtain scenario trees using a dynamic generation algorithm in order to satisfy the need to solve, in a reasonable period of time, complex optimization problems of optimal supply of wind power plants in electricity markets. The scenarios trees that are going to be obtained include information regarding the production of wind power energy and the clearing prices of the auctions of the different studied electricity markets.
In this study a scenario tree generation algorithm is presented, together with all the theoretical background needed to understand and assure a correct implementation of it, as well as the definition of the different agents that perform in the context of electricity markets. In addition to that, some data will be applied to this algorithm in order to obtain a representation of the scenario trees and to understand the interpretation of them. |
| DOI / handle | http://hdl.handle.net/2445/128065 |
| URL | Click Here |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |
Thu, 07/27/2017 - 13:55 — admin
| Publication Type | Tesis de Grau i Màster // BSc and MSc Thesis |
| Year of Publication | 2017 |
| Authors | Jordan Escandell Planells |
| Director | F.-Javier Heredia |
| Tipus de tesi | BSc Thesis |
| Titulació | Degree in Mathematics |
| Centre | Facultat de matemàtiques i Estadística. |
| Data defensa | 19/07/2017 |
| Nota // mark | 9 (A) |
| Key Words | teaching; unit commitment; energy; integer programming; electricity markets; robust formulations; BSc Thesis |
| Abstract | L’objectiu general és la caracterització de formulacions fortes del problema Unit Commitment. A més a més, l'estudi de les diferents desigualtats proposades pels diferents autors així com la seva adaptació i possible millora en la modelització de certs problemes reals de mercats elèctrics, constituïren l’enfoc principal de la feina a realitzar. Com a objectius específics tenim:
1. Entendre les diferents formulacions existents del UC, i estudiar-ne els seus punts forts i punts febles.
2. Aplicar la nova formulació escollida a la resolució de problemes reals, basats en informació extreta de les diferents fonts de les que disposàvem.
3. Entendre, interpretar i adaptar els codis proporcionats a la nova formulació considerada.
4. Obtenir resultats numèrics consistents amb la realitat, i que fossin aplicables a la vida real.
5. Millorar la metodologia existent, i aplicar-la per a la resolució de problemes de la vida real i obtenir solucions que satisfacin les capacitats dels diferents instruments que intervenen en el procés. |
| DOI / handle | http://hdl.handle.net/2117/106960 |
| URL | Click Here |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |
Wed, 07/19/2017 - 11:56 — admin
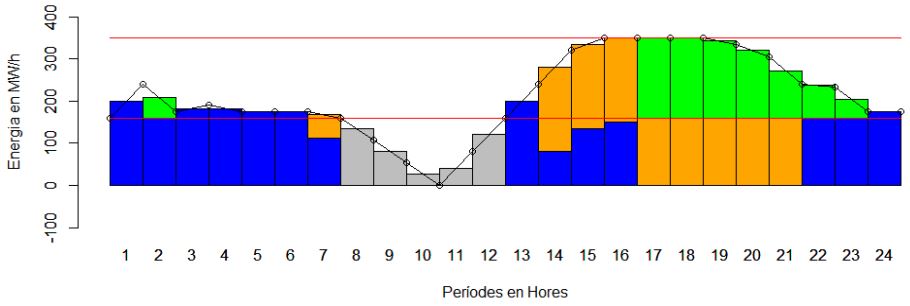 L'alumne del grau de matemàtiques de l'FME Jordan Escandell ha llegit el treball fi de grau Caracterització de Formulacions Fortes del Problema Unit Commitment. Aquest projecte abordava la caracterització de formulacions fortes del problema Unit Commitment a partir de l'estudi de les diferents desigualtats proposades pels diferents autors així com la seva adaptació i possible millora en la modelització de certs problemes reals de mercats elèctrics. Els models d'optimització matemàtica obtinguts s'han implementat computacionalment i aplicat a la resolució de problemes reals d'oferta òptima a merctas elèctrics. L'alumne del grau de matemàtiques de l'FME Jordan Escandell ha llegit el treball fi de grau Caracterització de Formulacions Fortes del Problema Unit Commitment. Aquest projecte abordava la caracterització de formulacions fortes del problema Unit Commitment a partir de l'estudi de les diferents desigualtats proposades pels diferents autors així com la seva adaptació i possible millora en la modelització de certs problemes reals de mercats elèctrics. Els models d'optimització matemàtica obtinguts s'han implementat computacionalment i aplicat a la resolució de problemes reals d'oferta òptima a merctas elèctrics.
Fri, 07/18/2014 - 23:26 — admin
 Miss Andina R. Brown defended last February 2014 the master thesis A multi-objective approach to infrastructure planning in the early stages of EV introduction. This thesis was developped at the Energy Economics Research Group of the Catalonia Institute for Energy Research (IREC) and the advisor were Dr. Cristina Corchero (IREC) and professor F.-Javier Heredia (GNOM). This study deals with the problem of a central planner wishing to install fast charging stations for electric vehicles applying a multi-objective approach to a real-case instance of the city of Barcelona. Miss Andina R. Brown defended last February 2014 the master thesis A multi-objective approach to infrastructure planning in the early stages of EV introduction. This thesis was developped at the Energy Economics Research Group of the Catalonia Institute for Energy Research (IREC) and the advisor were Dr. Cristina Corchero (IREC) and professor F.-Javier Heredia (GNOM). This study deals with the problem of a central planner wishing to install fast charging stations for electric vehicles applying a multi-objective approach to a real-case instance of the city of Barcelona.
Fri, 07/18/2014 - 22:44 — admin
| Publication Type | Tesis de Grau i Màster // BSc and MSc Thesis |
| Year of Publication | 2014 |
| Authors | Andina Rosalia Brown |
| Director | F.-Javier Heredia; Cristina Corchero |
| Tipus de tesi | MSc Thesis |
| Titulació | Master in Statistics and Operations Research |
| Centre | Faculty of Mathematics and Statistics |
| Data defensa | 27/01/2014 |
| Nota // mark | 9.0 |
| Key Words | multi-objective optimization; facility location; electric vehicle; fast charging stations; MSc Thesis |
| Abstract | This study approaches the problem from the perspective of a central planner wishing to install fast charging stations. A multi-objective approach is used to simultaneously consider two conflicting objectives in the optimisation problem. The first objective is to minimise the distance that potential consumers would need to deviate from their normal journeys in order to reach their nearest fast charging station, and thus minimise the associated inconvenience. The second objective is to minimise the set up costs associated with the installation of the stations, which differ according to the number of facilities installed and their location. These objectives are normalised using a function transformation and then combined into a single objective function. A mathematical model is formulated and implemented using GAMS to obtain results for the case study of Barcelona, building on the existing literature. Using the weighted sums method, multiple Pareto optimal solutions are found by solving for different relative weights combinations applied to the two objectives. These solutions are used to depict the Pareto front, offering insight into the nature of the trade-offs between the objectives and aiding the decision making process. This study develops the existing methodology used for the EV infrastructure problem, and shows how the application of a multi-objective formulation can offer useful insight to decision makers, particularly when preferences are unclear a priori. |
| DOI / handle | http://hdl.handle.net/2099.1/20851 |
| URL | Click Here |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |
Wed, 03/27/2013 - 11:21 — admin
| Publication Type | Tesis de Grau i Màster // BSc and MSc Thesis |
| Year of Publication | 2012 |
| Authors | Julian Cifuentes Rubiano |
| Director | F.-Javier Heredia |
| Tipus de tesi | MSc Thesis |
| Titulació | Master in Statistics and Operations Research |
| Centre | Faculty of Mathematics and Statistics |
| Data defensa | 21/12/2012 |
| Nota // mark | 9.5/10 |
| Key Words | teaching; stochastic programming; electricity markets; CO2 allowances; environment; emission limits; emission risk; CVaR; CEaR; modeling languages; MSc Thesis |
| Abstract | There are many factors that influence the day-ahead market bidding strategies of a generation company (GenCo) in the current energy market framework. Environmental policy issues have become more and more important for fossil-fuelled power plants and they have to be considered in their management, giving rise to emission limitations. This work allows to investigate the influence of both the allowances and emission reduction plan, and the incorporation of the derivatives medium-term commitments in the optimal generation bidding strategy to the day-ahead electricity market. Two different technologies have been considered: the coal thermal units, high-emission technology, and the combined cycle gas turbine units, low-emission technology. The Iberian Electricity Market and the Spanish National Emissions and Allocation Plans are the framework to deal with the environmental issues in the day-ahead market bidding strategies. To address emission limitations, some of the standard risk management methodologies developed for financial markets, such as Value-at-Risk (VaR) and Conditional Value at Risk (CVaR), have been extended. This study offers to electricity generation utilities a mathematical model to determinate the individual optimal generation bid to the wholesale electricity market, for each one of their generation units that maximizes the long-run profits of the utility abiding by the Iberian Electricity Market rules, the environmental restrictions set by the EU Emission Trading Scheme, as well as the restrictions set by the Spanish National Emissions Reduction Plan. The economic implications for a GenCo of including the environmental restrictions of these National Plans are analyzed and the most remarkable results will be presented.. The problem to be solved in this project will provide generationutilities with a mathematical tool to find the individual optimal generation bid for each one of theirgeneration units that maximizes the long-run profits of the utility abiding by the Iberian ElectricityMarket rules, the environmental restrictions of the EU Emission Trading Scheme and also by theSpanish National Emissions Reduction Plan |
| DOI / handle | http://hdl.handle.net/2099.1/17485 |
| URL | Click Here |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |
Thu, 07/19/2012 - 21:10 — admin
| Publication Type | Tesis de Grau i Màster // BSc and MSc Thesis |
| Year of Publication | 2012 |
| Authors | Lucia Igualada González |
| Director | F.-Javier Heredia; Cristina Corchero |
| Tipus de tesi | Tesi Final Màster // MSc Thesis |
| Titulació | Master in Statistics and Operations Research |
| Centre | Faculty of Mathematics and Statistics |
| Data defensa | 04/07/2012 |
| Nota // mark | 10 MH // 10/10 |
| Key Words | research; teaching; smartgrids; microgrid; migrogrid central controller; electric vehicle; MSc Thesis |
| Abstract | Smart grids and microgrids are the key in the near future where a decentralization of energy generation is expected. From the point of view of microgrid energy management, economic scheduling for generation devices, storage systems and loads is a crucial problem. Performance an optimization process is necessary to minimize the operating costs while several operational constraints are taken into account. Energy management is carried out by MCC (Microgrid Central Controller) in three steps: tertiary, secondary and primary controls. Tertiary control is executed one day-ahead and has two objectives. The �first is an economic optimization using a program based on an Economic Dispatch and an Unit Commitment problem. The second objective is to improve the por�tability of the supply and demand balance by interacting with the grid and taking advantage of the V2G (vehicle-to-grid) capability of the charging spot, and to generate a schedule over all components of the microgrid. The secondary control receives the scheduling plan created by tertiary control and taking into account current data, corrects the power outputs of generation units. Exchanged power with the grid and storage states of charge programmed by the tertiary control are ensured. This Energy Management System has been tested over different scenarios. One of them is based on a smart house with a photovoltaic module, a micro wind turbine and one electric vehicle charging spot. The other scenario is based on a large building where one micro gas turbine and one storage device have been added to the rest of units. After analysing the results, several conclusions have been deduced such as a change in curve of load and a lower cost for the user. Generally, the consumption over peak periods is decreased or is almost zero in some test cases, while the demand overnight is increased. |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |
Thu, 07/19/2012 - 17:05 — admin
Thu, 07/19/2012 - 17:02 — admin

|
 L'alumne del grau de matemàtiques de l'FME Jordan Escandell ha llegit el treball fi de grau Caracterització de Formulacions Fortes del Problema Unit Commitment. Aquest projecte abordava la caracterització de formulacions fortes del problema Unit Commitment a partir de l'estudi de les diferents desigualtats proposades pels diferents autors així com la seva adaptació i possible millora en la modelització de certs problemes reals de mercats elèctrics. Els models d'optimització matemàtica obtinguts s'han implementat computacionalment i aplicat a la resolució de problemes reals d'oferta òptima a merctas elèctrics.
L'alumne del grau de matemàtiques de l'FME Jordan Escandell ha llegit el treball fi de grau Caracterització de Formulacions Fortes del Problema Unit Commitment. Aquest projecte abordava la caracterització de formulacions fortes del problema Unit Commitment a partir de l'estudi de les diferents desigualtats proposades pels diferents autors així com la seva adaptació i possible millora en la modelització de certs problemes reals de mercats elèctrics. Els models d'optimització matemàtica obtinguts s'han implementat computacionalment i aplicat a la resolució de problemes reals d'oferta òptima a merctas elèctrics.
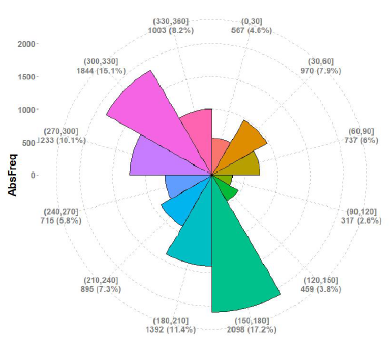 On June 2014 two new Master Thesis of the Master of Statistcs and Operations Research UPC-UB was presented
On June 2014 two new Master Thesis of the Master of Statistcs and Operations Research UPC-UB was presented
 Miss Andina R. Brown defended last February 2014 the master thesis A multi-objective approach to infrastructure planning in the early stages of EV introduction. This thesis was developped at the Energy Economics Research Group of the Catalonia Institute for Energy Research (IREC) and the advisor were Dr. Cristina Corchero (IREC) and professor F.-Javier Heredia (GNOM). This study deals with the problem of a central planner wishing to install fast charging stations for electric vehicles applying a multi-objective approach to a real-case instance of the city of Barcelona.
Miss Andina R. Brown defended last February 2014 the master thesis A multi-objective approach to infrastructure planning in the early stages of EV introduction. This thesis was developped at the Energy Economics Research Group of the Catalonia Institute for Energy Research (IREC) and the advisor were Dr. Cristina Corchero (IREC) and professor F.-Javier Heredia (GNOM). This study deals with the problem of a central planner wishing to install fast charging stations for electric vehicles applying a multi-objective approach to a real-case instance of the city of Barcelona.
